This is the year — you just know it. You finally gave that side gig you’ve been dreaming about a real shot and it’s starting to pay off in more ways than you thought. What started out as just a hobby for baking quickly turned into opening your very own brick-and-mortar bakery on the corner. Now, you’re left wondering if it’s time to take the next step and make your side hustle your full-time job, but you want to make sure it’s the right financial decision.
In this post, we’ll teach you how to measure the efficiency and profitability of your company by using the gross profit formula, to help you understand if you’re making the right decision. By subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from your revenue, you can find the gross profit, and make data-driven decisions about where to invest and where to save.
Calculating profit margins allows you to clearly see if your side job is ready to turn into a full-time business.
How to Calculate Gross Profit
Gross profit, also known as gross income, uses variable costs to measure efficiency. It is the leftover profit after you deduct the costs associated with providing a service or making and selling a product. These variable costs, like shipping and raw materials, change based on production levels, unlike fixed costs that remain constant each month like salary, rent, and marketing costs.
The higher your gross profit, the more efficient your company is at using supplies and labor to produce goods or services. Gross profit is a dollar amount that can you can calculate using the following formula:
Gross Profit = Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Revenue
Revenue is the total amount of money your company brings in from the sale of products or services during a specific period. This is your total income before any deductions and can be found on the top line of your income statement.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Cost of goods sold are the manufacturing costs associated with producing and delivering your products or services. These are the variable costs that don’t take into account any fixed costs.
Examples of COGS:
- Production equipment costs
- Shipping costs
- Production utilities
- Raw materials
- Packaging
- Production labor costs

Example of Using the Gross Profit Formula
Now let’s look at how to calculate the gross profit of your bakery for the year.
First, you’ll need to calculate the total revenue — the total amount of money your customers paid over the last year for your baked goods. Looking at your yearly income statement, you see that your total sales were $375,000.
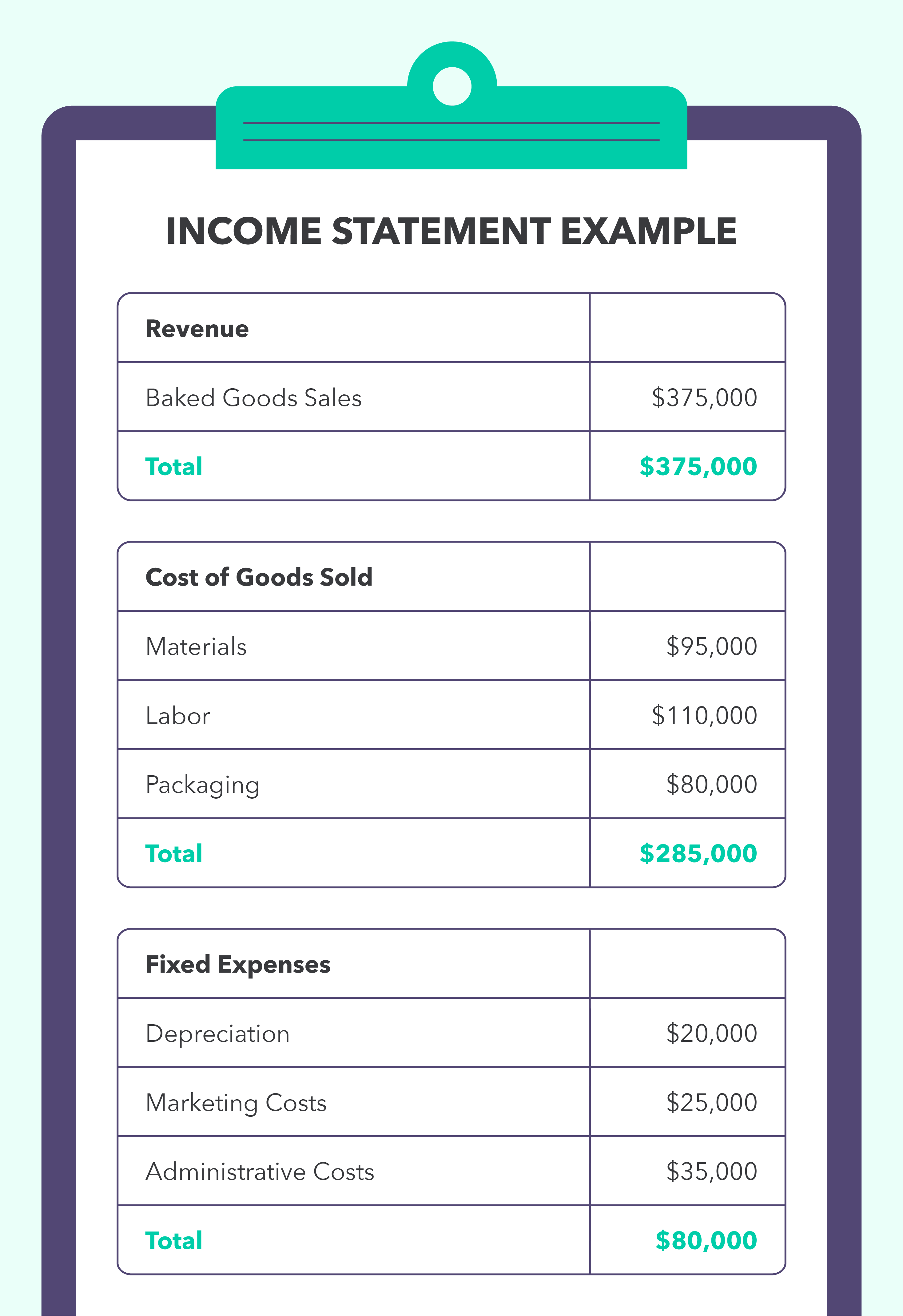
Next, you’ll calculate your COGS by looking at how much you spent on labor, materials, and packaging throughout the year. Looking at your income statement, you determine that your COGS is $285,000.
Using the gross profit formula, subtracting $285,000 (COGS) from $375,000 (revenue), you end up with a gross profit of $90,000 for the year for your bakery. You’ll notice that we didn’t factor in any of the fixed expenses — these will come in later when we calculate net profit.
How To Calculate Gross Profit Margin
Gross profit margin, also known as gross margin, uses the gross profit calculation divided by the total revenue, then multiplied by 100 to determine the profitability percentage of your manufacturing and production processes. You can calculate gross profit margin by using the following formula:
Gross Profit Margin = [Gross Profit / Revenue] x 100
Gross profit margin is simply a way to show your gross profit in a ratio or a percentage, instead of a dollar amount. You can calculate this monthly or annually using your income statements, but in order to get a real sense of your company’s performance, you’ll want to compare your profit margins to previous months or years. This will allow you to see if margins are growing or decreasing and inform your decisions on making adjustments as needed.
Example of Using the Gross Profit Margin Formula
Let’s use the same income statement we used before to now calculate the gross profit margin. By subtracting $285,000 (COGS) from $375,000 (revenue), you found that your gross profit was $90,000.
Now, let’s take that $90,000 and divide it by the total revenue of $375,000. This gives you 0.24 which you’ll then multiply by 100. This equals 24 percent, meaning that your bakery had a gross profit margin of 24 percent for the year.
Gross Profit vs. Net Profit
The key to understanding how your company is doing financially is knowing your gross profit and net profit, also known as gross income and net income. Gross profit measures the productivity of manufacturing and production processes, while net profit measures the company’s productivity as a whole. To find the net profit, you’ll use the following formula:
Net Profit = Revenue – Total Costs
Total Costs = Cost of Goods Sold + Taxes + Overhead Expenses
This is where those other fixed expenses will come in, so let’s look at that income statement again to calculate your net profit for the year.
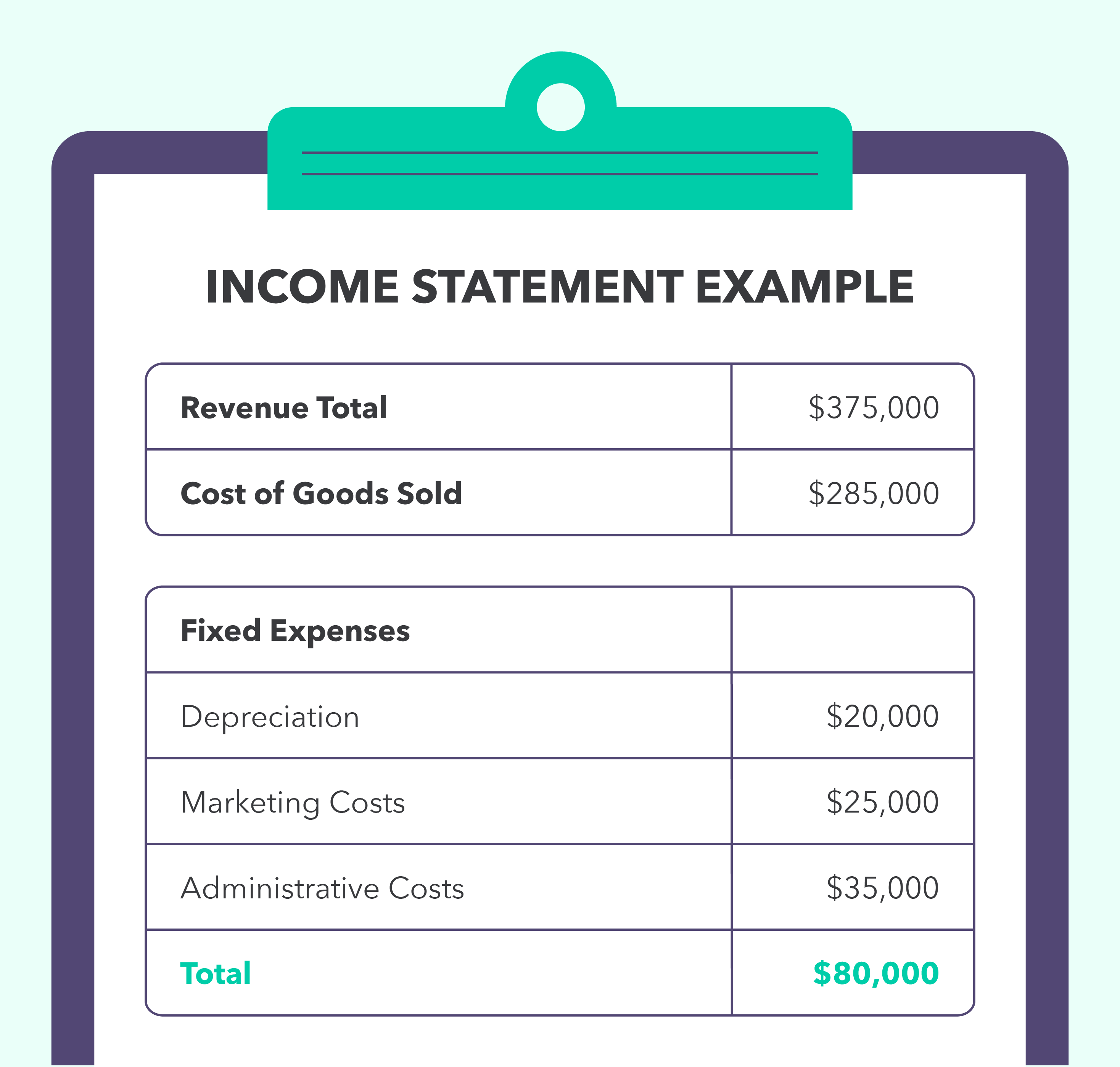
Looking at your income statement, you can see that your COGS is $285,000 and your total expenses are $80,000. Let’s add those, making your total costs $365,000. Now, you’ll subtract $365,000 (total costs) from $375,000 (revenue) to give you a net profit of $10,000 for the year.
How to Calculate Net Profit Margin
Net profit margin, like gross profit margin, is a way to show the net profit in a ratio or percentage. It can be calculated using the following formula:
Net Profit Margin = [Net Profit / Revenue] x 100
Looking at that same income statement, you can calculate net profit margin by taking your net profit of $10,000 and dividing it by your total revenue of $375,000. This gives you 0.02, which you’ll then multiply by 100 to equal 2.7 percent. This means that your bakery had a net profit margin of 2.7 percent for the year.
Average Profit Margins
So, now that you’ve calculated your gross profit margin and net profit margin, how do you know if it’s good? Looking at average profit margins for your industry can help you determine if you’re on the right track or need to make adjustments.
If you compare your bakery’s gross profit margin of 24 percent and net profit margin of 2.7 percent with the average profit margins of 25 percent and 1.1 percent respectively from businesses in the retail (grocery and food) industry, you’ll see that your profitability levels are where they should be.
How to Improve Profit Margins and Grow Your Business
Knowing your gross profit margin and net profit margin allows you to make important financial decisions for your company based on data. If you compare your gross profit margin with industry averages and find that it’s lower than it should be, here are some things you can do.
- Increase Productivity: Consider how you can serve more customers in less time by making small tweaks to your process that increase efficiency. These can be things like making one batch of frosting that can be used for multiple kinds of cupcakes, rearranging your assembly line to save time, or prepping dry ingredients for recipes ahead of time.
- Decrease COGS: Cut labor costs by training your employees on multiple skills instead of hiring additional people, find a cheaper way to source your materials like buying in bulk, or find less expensive shipping alternatives.
- Increase Prices: To offset costs, especially when the economy is unstable, you can raise the prices of your products. Make sure you’re careful not to raise prices too high though, causing a drop in sales.
Assessing your company’s utilization and profitability helps you make sound decisions and see if your side hustle is ready to turn into a full-time business.
Creating a business budget is a great way to plan for expenses and track your cash flow, so you’re not surprised by your profit margins at the end of the year. Download our free Mint app to track your business goals, create budgets, and see where your money is going, so you can get one step closer to financial freedom.
Sourcing:
-
Previous Post
Finance Tips for the Self-Employed







